
In some cases, we earn commissions when sales are made through our referrals. These financial relationships support our content but do not dictate our the cost principle is used recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates products based on thousands of hours of research. Learn more about our full process and see who our partners are here. While the cost principle seems advantageous, it may not be every business’s best method.
- We canillustrate each account type and its corresponding debit and crediteffects in the form of an expandedaccounting equation.
- Since liabilities, equity (such as common stock), and revenues increase with a credit, their “normal” balance is a credit.
- These statements are discussed indetail in Introduction to Financial Statements.
- Most of the public-owned companies apply GAAP in accounting; it is a requirement that they also use historical cost principle.
- This ensures your assets are based on their initial costs versus their market value over time.
What are the other principles of GAAP?

This is particularly relevant for long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, which may have appreciated over time. By adhering to the Cost Principle, financial statements accurately reflect the value of the assets at the time of acquisition, providing a reliable basis for decision-making. In the realm of accounting, the Cost Principle, also known as the Historical Cost Principle, stands as a fundamental guideline shaping the way assets are recorded and reported on financial statements. This principle is deeply embedded in accounting standards, providing a structured approach to valuing assets based on their original acquisition cost.
Explanation of Accrual Accounting
By avoiding subjective estimates or valuations, the Cost Principle enhances the credibility of financial reporting. Overall, the application of the Cost Principle ensures that financial statements provide a reliable and objective representation of a company’s assets. https://www.bookstime.com/articles/enrolled-agent-exam It contributes to the consistency and comparability of financial reporting, allowing stakeholders to make informed assessments of an entity’s financial position. By using accrual accounting, businesses can avoid distortions in their financial statements caused by timing differences between when cash is exchanged and when the related economic activity takes place. This allows for a more comprehensive representation of a company’s financial position and performance.
- The cost principle, also known as thehistorical cost principle, states that virtually everything thecompany owns or controls (assets)must be recorded at its value at the date of acquisition.
- Depending on theaccount type, the sides that increase and decrease may vary.
- This transparency is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and meeting regulatory requirements, particularly in sectors where accurate asset valuation is essential for compliance and risk management.
- The ongoing pursuit of more relevant and reliable financial reporting has led to alternative valuation methods, such as fair value accounting.
- As companies may have acquired similar assets at different times and prices, the recorded values of those assets may not accurately reflect their actual values or current market prices.
Time Period Assumption
- The Cost Principle can also lead to outdated information in financial statements.
- If it is worth less than the value on the books, then the goodwill is considered to be impaired.
- Even though the customer has not yet paid cash, there is a reasonable expectation that the customer will pay in the future.
- The SEC regulates the financial reporting of companies selling their shares in the United States, whether US GAAP or IFRS are used.
- Using cost principle follows the Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures (GAAP), which is established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
- This historic cost of an asset is used to provide reliable and consistent records.
Some companies that operate on a global scale may be able to report their financial statements using IFRS. The SEC regulates the financial reporting of companies selling their shares in the United States, whether US GAAP or IFRS are used. The basics of accounting discussed in this chapter are the same under either set of guidelines. Cost principle offers accurate information regarding the amount received from a sale. The numbers need to be the exact like the actual expenses from business transactions from a specific period. The basic accounting principle is that all the cost principle accounting information needs to be based on a cash or cash-equivalent principle.
CompanyCompany
The concept of the T-account wasbriefly mentioned in Introduction to Financial Statements and will be used laterin this chapter to analyze transactions. A T-account is called a“T-account” because it looks like a “T,” as you can see with theT-account shown here. For example, a school year is broken down into semesters orquarters. After each semester or quarter, your grade point average(GPA) is updated with new information on your performance inclasses you completed.

What Is The Cost Principle In Accounting

Stakeholders relying on these figures for decision-making might find themselves working with outdated or incomplete information. In accounting, the cost principle is a foundational concept that dictates how assets are recorded on financial statements. This principle requires that assets be listed at their original purchase price rather than their current market value. Another drawback of the Cost Principle is that it does not consider the impact of inflation. Over time, the purchasing power of money decreases due to inflation. However, the Cost Principle does not account for this decrease in purchasing power when recording assets at their original cost.
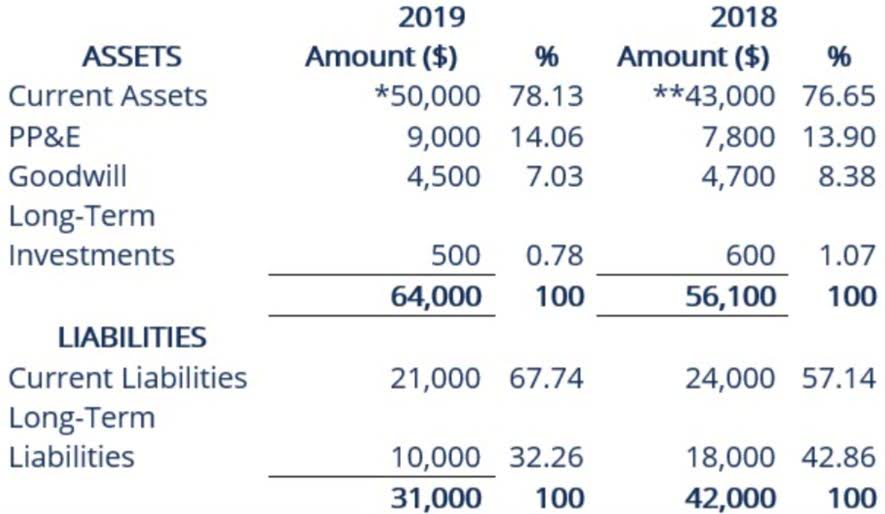
By adhering to the principle, financial statements provide a reliable and objective representation of a company’s financial position, ensuring consistency and comparability for stakeholders. One of the key advantages of the Cost Principle is its objectivity. The principle requires assets to be recorded at their original cost, which is a verifiable and objective measure. This provides users of financial statements with a consistent basis for assessing the value of assets owned by a company.
The rationale behind the Cost Principle is to ensure objectivity and provide users of financial statements with information that is verifiable and reliable. By recording assets at https://x.com/BooksTimeInc their original cost, the principle aims to provide a true and accurate representation of the resources owned by an entity at a specific point in time. A debit records financial information on theleft side of each account.

